How has the 2016 Sally Hess internship affected me? Truthfully, it’s hard to describe all the minute ways in which I have grown while working with the Hingham Historical Society this summer. The opportunity to serve as the 2016 Sally Hess Intern has aided me in a good deal of self-discovery and helped launch my development as a museum professional.
Here’s a little background about myself— I went to college with an inkling of an idea for what I might have wanted to study as a major: a high school teacher had assigned an art history paper in which we had to describe work of a Renaissance painter. This sparked curiosity for a subject that I had never before encountered. My high school didn’t offer any art history courses so I gave it a shot my freshman year of college. It just so happened that I had stumbled across the subject that kindled an intense yearning to know more—a craving which I hope everyone feels at some point in their lives.
So, after four determined years of study I graduated college in May 2016 with my Bachelor’s degree. Coming back to one’s hometown after such a momentous occasion doesn’t always feel so glorious; however, I took this anticlimactic feeling to propel my next steps, which included reaching out to the Hingham Historical Society in hopes that they might have some niche for me to work with them. While I waited for them to respond to my inquiry, my mind kept returning to the typical questions a newly graduated individual deliberates: what do I want to do with my degree? Where should I look for work? What work is there for someone with my focus? Needless to say, I was feeling restless, nervous, and a little dire.

Eve Fairbanks working with a wool winder at the Old Ordinary, our 1688 house museum
Then, in a rather timely fashion, the Historical Society responded, interviewed me, and decided to award me their Sally Hess Internship for the summer of 2016. Thus I found myself with a paid internship with a great organization. Over the months I’ve been working with them, I have been exposed to many facets of the museum world that had never even seemed an option for me. For example, I consider myself a “public-speaking-aphobe.” The Sally Hess Internship required me to act as a docent at the Historical Society’s 1688 house museum, known as the Old Ordinary. This opportunity took me out of my comfort zone but I soon overcame some of that initial nervousness I have with presenting myself. I learned the rooms inside and out by watching other tour guides and reading the material the Hingham Historical Society provided for me. By the fifth tour I gave on my own, visitors to the Old Ordinary were not only commenting on the extraordinariness of the building but also on the quality of my tours. I also experienced the collections work done at a museum: cataloguing 17th– 20th century artifacts, entering new files into our collections database, and researching the history and significance of objects in our collection. I have fallen even more deeply in love with the museum world and have confronted many of those haunting post-graduation thoughts I previously mentioned.

Sally Hess intern Eve Fairbanks catalogued the numerous architectural elements from local buildings in the John P. Richardson Collection at the Hingham Historical Society.
I now feel as though I have a direction I want to head in. I’ve confirmed with myself that I might enjoy museum work as a career. I plan to seek out other opportunities working with documentation of artifacts, helping organize behind the scenes at a museum, or (who knows) maybe even giving more tours. The notion of going back to school for a Master’s degree doesn’t seem so far-fetched; now, that I feel a new verve for this business. I am so grateful that the Hingham Historical Society gave me a chance to work with them. I will never forget this experience and can’t wait to see where it leads me.
Thanks infinitely,
Eve












 His son,
His son,  The Hingham Agricultural and Horticultural Society, founded in 1869, was also comprised of local men and women, many of whom were involved in industry, trade, and commerce. (Here, they pose for a formal portrait in front of Hingham’s Agricultural Hall in the late 1880s or early 1890s.) As a society, they were earnestly dedicated to scientific farming, that is, using the progressive values of the 19th century and the power of new knowledge and industrial technology to “improve” agriculture along “modern” lines. At the agricultural fair each fall, prizes offered in different categories attracted many entrants. One could win a medal or ribbon—and an accompanying cash prize–for anything from crops and livestock to flowers and preserves.
The Hingham Agricultural and Horticultural Society, founded in 1869, was also comprised of local men and women, many of whom were involved in industry, trade, and commerce. (Here, they pose for a formal portrait in front of Hingham’s Agricultural Hall in the late 1880s or early 1890s.) As a society, they were earnestly dedicated to scientific farming, that is, using the progressive values of the 19th century and the power of new knowledge and industrial technology to “improve” agriculture along “modern” lines. At the agricultural fair each fall, prizes offered in different categories attracted many entrants. One could win a medal or ribbon—and an accompanying cash prize–for anything from crops and livestock to flowers and preserves.





 A new exhibit opened today at our 1688
A new exhibit opened today at our 1688 

 After his trip west Sprague returned briefly to the South Shore, working as a clerk in a Nantasket Beach hotel until, the following year, he started to work as an illustrator for prominent American botanist
After his trip west Sprague returned briefly to the South Shore, working as a clerk in a Nantasket Beach hotel until, the following year, he started to work as an illustrator for prominent American botanist  Hingham pulled out all the stops in preparation for its 300th anniversary celebration. Twelve hundred of the Town’s residents participated in a three-plus hour historical pageant, which was performed before 2,000 attendees on the evenings of June 27, 28, and 29, 1935. In the midst of the Great Depression, the Town appropriated an astonishing $14,000 for its tercentenary observance, which was written and directed by
Hingham pulled out all the stops in preparation for its 300th anniversary celebration. Twelve hundred of the Town’s residents participated in a three-plus hour historical pageant, which was performed before 2,000 attendees on the evenings of June 27, 28, and 29, 1935. In the midst of the Great Depression, the Town appropriated an astonishing $14,000 for its tercentenary observance, which was written and directed by 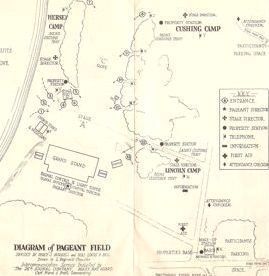 “The Pageant of Hingham” was performed on a sprawling outdoor set at what was then called
“The Pageant of Hingham” was performed on a sprawling outdoor set at what was then called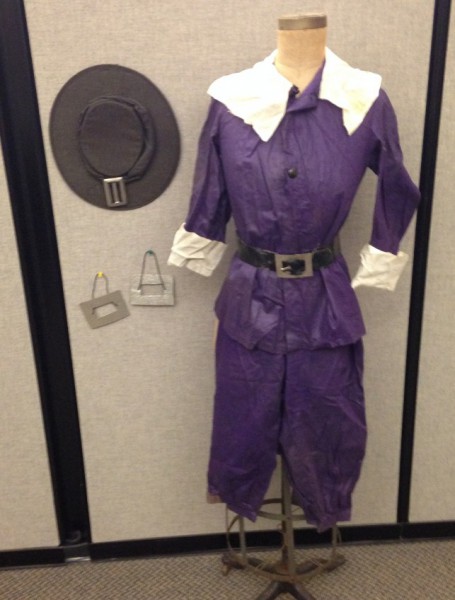 
 Young Newell and Herbert Cole, another Hingham boy also cast as an 18th century Hingham boy (Perez Cushing, 1746-1794), called out the names of the guests arriving at the Cushing farm. An example of their lines, taken from the Pageant Program:
Young Newell and Herbert Cole, another Hingham boy also cast as an 18th century Hingham boy (Perez Cushing, 1746-1794), called out the names of the guests arriving at the Cushing farm. An example of their lines, taken from the Pageant Program:
 These seven Hingham boys posed with three bicycles are witnessing the birth of modern cycling. Behind them are two older bicycles—so-called “high wheelers” or “penny farthings” (the latter nickname descriptive of the relative sizes of the two wheels). High-wheelers originated in England and became popular in the United States in the early 1880s. As this photo lets us see clearly, these early bicycles had a “direct drive” mechanism, that is, the pedals attach directly to the wheel, so that the cyclist’s motion turns the wheel directly. Enlarging the front wheel, therefore, was the only way to make the bicycles go faster–and this is what happened. Front wheels often five feet in diameter, with the cyclist perched directly over the wheel, meant an increased risk of the cyclist pitching headfirst from the front of his bike. Cycling in the era of the high wheelers was a sport for athletic young men.
These seven Hingham boys posed with three bicycles are witnessing the birth of modern cycling. Behind them are two older bicycles—so-called “high wheelers” or “penny farthings” (the latter nickname descriptive of the relative sizes of the two wheels). High-wheelers originated in England and became popular in the United States in the early 1880s. As this photo lets us see clearly, these early bicycles had a “direct drive” mechanism, that is, the pedals attach directly to the wheel, so that the cyclist’s motion turns the wheel directly. Enlarging the front wheel, therefore, was the only way to make the bicycles go faster–and this is what happened. Front wheels often five feet in diameter, with the cyclist perched directly over the wheel, meant an increased risk of the cyclist pitching headfirst from the front of his bike. Cycling in the era of the high wheelers was a sport for athletic young men.







