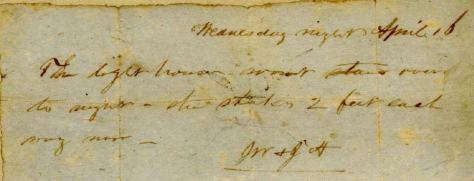In 1857, eleven year-old Francis Lincoln of Hingham described his family’s Thanksgiving in a school essay. As we would today, he writes of roast turkey, a multi-generational family gathering, and giving thanks to God:
Thanksgiving was the day set apart from work by our forefathers to worship God, after they had gathered in their harvest, and it has been celebrated ever since their time. It is the occasion when Grandmothers, Grandfathers, Uncles, Aunts, Cousins, Brothers and Sisters gather together and have a good dinner of Roast Turkey and Plum-Pudding. I have generally dined at my Grandfather’s, but since he has been unwell and rather old, I have remained at home. I will give you an account of my last Thanksgiving Day. In the morning, I attended church and heard the Rev. Calvin Lincoln preach an excellent sermon. In the afternoon my Father, two brothers and I started on a walk to World’s End, which is more than two miles from our house, but we went to the point which made the walk about one half a mile longer. Solomon then loaded his gun and fired at a target, he also let Arthur fire at an old stump. We got home at about five and a half o’clock having been gone three hours. I therefore spent a very pleasant Thanksgiving.
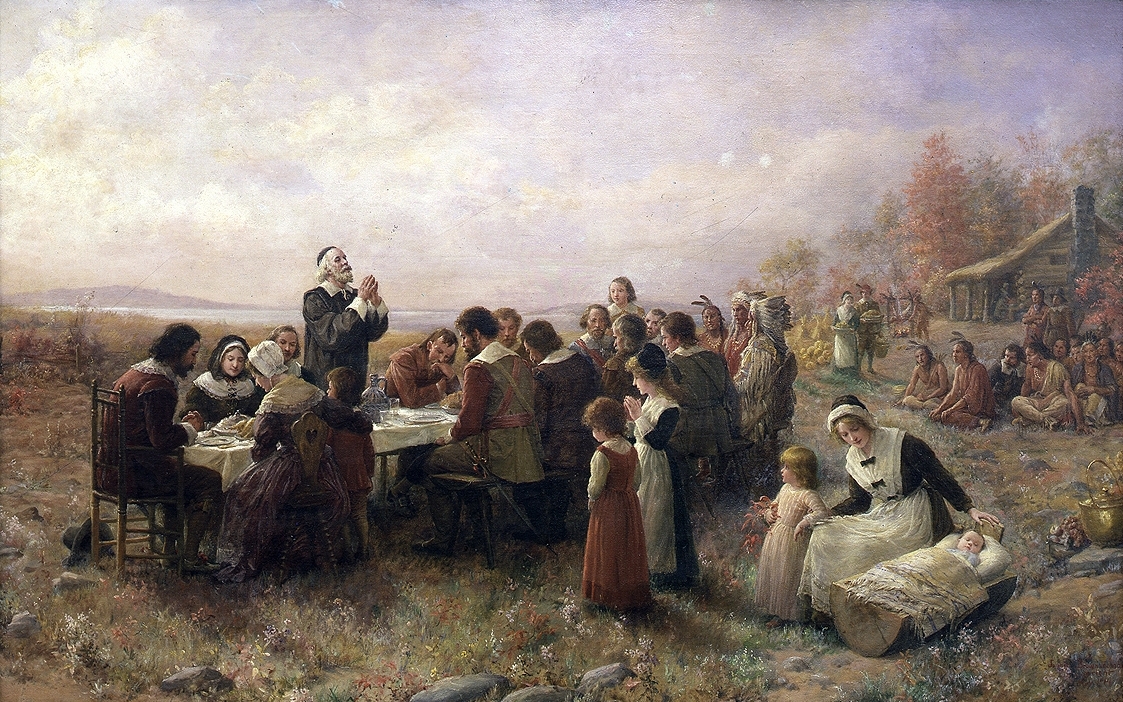
Yet, from our 21st century perspective, two things are missing from Lincoln’s essay: football, of course, which did not yet exist in its modern form, and any mention of the Pilgrims –because the now-universal association of Plymouth, the Pilgrims, and Thanksgiving Day is a relatively recent phenomenon.
The Puritan settlers of New England had a tradition of “providential” holidays: days of fasting during difficult times for the community and days of thanksgiving to celebrate times of plenty or deliverance from strife. In the years following the American Revolution, our federal government adopted this practice and held periodic thanksgiving holidays, including one declared by newly-elected President Washington in 1789. The practice gradually became institutionalized, and in 1816 Massachusetts and New Hampshire became the first two states to establish late fall state holidays of Thanksgiving. During the depths of the Civil War, in a bid to foster unity, Abraham Lincoln declared a national Thanksgiving holiday. All were framed in religious terms not unlike the early settlers’ days of thanksgiving.
The Pilgrims were not ignored in 18th and 19th century New England; we just did not always think of them and turkey dinners at the same time. Rather, in Plymouth, Boston, and other Massachusetts towns, dinners, speeches, parades, and other celebrations were held on December 22, the anniversary of the date in 1620 when the Pilgrims landed at Plymouth (having already spent several months on Cape Cod). Speeches and sermons were given, on what came to be called Forefathers’ Day, by South Shore ministers and politicians, as well as the occasional national luminary, such as John Quincy Adams (1802), Daniel Webster (1820), Edward Everett (1824), and Lyman Beecher (1827). The focus, however, was on the Pilgrims’ landing at Plymouth Rock and their role as our nation’s “founding fathers.”
So, what led to the rise of the popular story of the “first Thanksgiving?” To a great extent, it was the product of social and political currents in post-Civil War America. Interest in the Pilgrims and our “founding fathers” grew with white Protestant America’s increased anxiety over immigration and the influx of newcomers with diverse backgrounds. A myth of non-violent colonialism was a balm to the conscience of a nation that had achieved its “manifest destiny” of expansion across the continent.
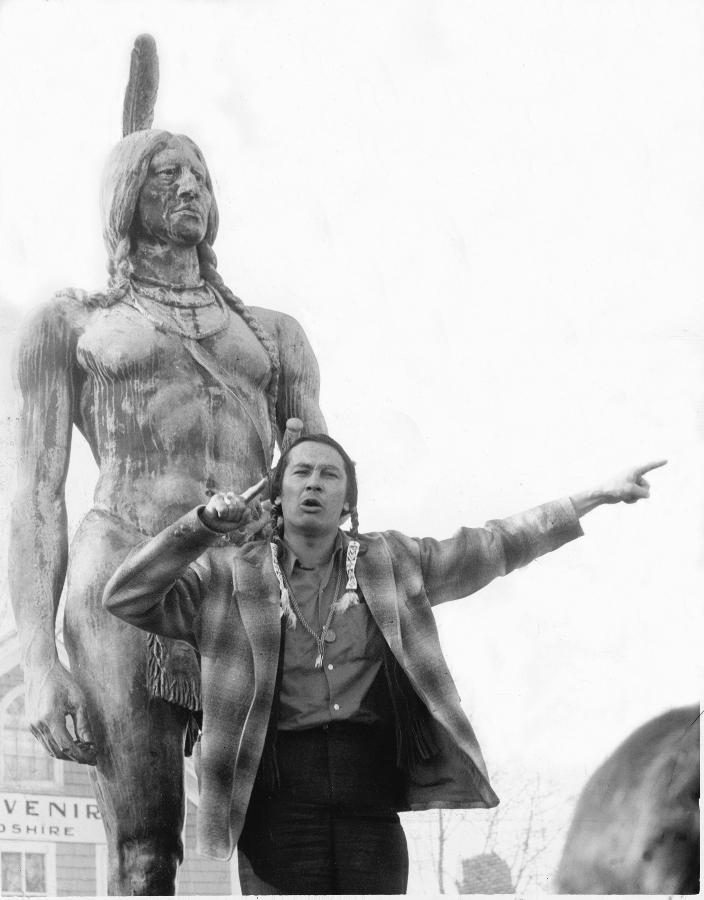


In 1970, 350 years after the Pilgrims’ landing at Plymouth, representatives of the Wampanoag declared a National Day of Mourning on the fourth Thursday in November, to honor their ancestors and educate those celebrating a “traditional” (though no more than 100 year-old) Thanksgiving about white America’s treatment of their people. This “counter-commemoration” has its own 50th anniversary as Plymouth observes its 400th this year. Growing recognition of the checkered history that lies behind the “First Thanksgiving” is the result of the attention that has been paid to Native American history in New England and a more critical examination of the late 19th and early 20th century version of that story. This itself is resulting in a further evolution of the holiday’s meaning, including a greater emphasis on celebrating our families and fellowship in the present day.
[First posted in Nov. 2014; edited in Nov. 2020]